نحوه یادگیری زبان انگلیسی با این پادکست
ابتدا خلاصه فارسی این پادکست انگلیسی با متن را مطالعه کنید تا دید کلی از موضوعی که در پادکست صحبت میشود به دست بیاورید. بعد از آن فایل صوت را پخش کنید و همراه با متن پیش بروید. یک مرتبه کامل گوش کنید و سعی کنید تا حد امکان متوجه موضوعات شوید. در انتها لغات جدیی که بلد نبودید را پیدا کنید و یادبگیرید. حالا دوباره پادکست را با متن گوش کنید و ببینید. شیوه یادگیری را به ترتیب برای شما در زیر نوشتهایم حتما طبق آن پیش بروید.
- مطالعه خلاصه فارسی پادکست
- گوش دادن به پادکست همراه با مشاهده متن انگلیسی
- پیدا کردن و یادگیری لغات جدید
- گوش دادن مجدد به پادکست همراه با متن انگلیسی
- گوش دادن به پادکست بدون متن
- پاسخ به آزمون مربوط به پادکست
خلاصهای از پادکست انگلیسی داروی جدید آلزایمر
مقامات بهداشتی ایالات متحده هفته گذشته یک داروی جدید برای آلزایمر را تایید کردند. این دارو به نام لکمبی است و اولین دارویی است که باعث کاهش افت حافظه تا چند ماه میشود. اتحادیه آلزایمر، آلزایمر را به عنوان یک بیماری مغزی توصیف میکند که منجر به کاهش حافظه، تفکر و مهارتهای استدلالی میشود.
یکی از شایعترین نشانههای بیماری آلزایمر فراموش کردن اطلاعات یا تاریخها و رویدادهای به تازگی یاد گرفته شده است. افراد مبتلا به این بیماری دچار مشکلاتی در انجام کارهایی میشوند که قبلاً انجام میدادند. برخی از آنها مشکلی در پیوستن به یک گفتگو یا دنبال کردن آن دارند. لکمبی که به تازگی تایید شده، درمان جدیدی بود که برای این بیماری به آن نیاز بود.
اما متخصصان هشدار میدهند که این دارو درمان نهایی نیست. دکتر جوی اسنایدر، یک پزشک متخصص مغز در دانشگاه واشنگتن در سنت لوئیس، میزوری، میگوید: “این دارو درمان نهایی نیست. این امر مانع بدتر شدن افراد نمیشود، اما به طور قابلتوجهی روند پیشرفت بیماری را کاهش میدهد.” وی اضافه میکند: “این ممکن است به این معنی باشد که کسی میتواند بین شش ماه تا یک سال دیگر بتواند رانندگی کند.”
اداره غذا و داروی آمریکا (FDA) این دارو را از طریق یک روند سریعتر از معمول تأیید کرد. این روند اجازه میدهد که داروها بر اساس نتایج اولیه عرضه شوند. این دارو فقط برای بیماران در مرحله اولیه قابل استفاده است و نیازمند تزریق توسط کارکنان بهداشتی هر دو هفته یک بار است. هنوز مشخص نیست که این دارو چقدر میتواند به افراد مبتلا به بیماری کمک کند. همچنین نگرانیهایی درباره ایمنی آن وجود دارد.
با این حال، دکتر ریچارد هودز، مدیر مؤسسه ملی پیری، میگوید: “این یک انقلاب است. کافی نیست، اما خوشحال کننده است که ما میتوانیم کاری انجام دهیم.” وی اضافه میکند: “چند ماه با شناخت بهتر، ارزشش براتون چقدره؟”
این دارو جدید چگونه کار میکند؟
لکمبی توسط شرکت آیسای ژاپن و شریک آمریکایی آن بیوجن تولید میشود. این دارو طراحی شده است تا به طور مستقیم با بتا-آمیلوئید، یک مادهای که در مغز ایجاد میشود و به آلزایمر منجر میشود، تداخل کند و آن را برطرف کند. دکتر سام گندی، متخصص آلزایمر در بیمارستان ماونت ساینای نیویورک، به آژانس خبری AP گفت که لکمبی با هدف تداخل با یک شکل کمی متفاوت از آمیلوئید نسبت به سایر داروهای آزمایشی درمان بیماری، به نتایج موفقیتآمیز رسید. این میتواند توجیه کند که چرا بسیاری از داروهای آزمایشی دیگر شکست خوردهاند.
در سال ۲۰۲۱، مقامات بهداشتی آمریکا داروی مشابهی به نام آدوهلم را تأیید کردند، اگرچه مطالعات هرگز ثابت نکرد که واقعاً به بیماران کمک میکند. این تصمیم منجر به انتقاداتی پس از یک تحقیق کنگره شد.
اثربخشی لکمبی چقدر است؟
در مطالعه ۱۸ ماهه آیسای در مورد تقریباً ۱۸۰۰ نفر، لکمبی بهنظر میرسد پیشرفت بیماران در مرحله اولیه را تا ۵ ماه به تأخیر میاندازد. در این مطالعه، افراد بر اساس یک مقیاس ۱۸ امتیازی که تواناییهای ذهنی و عملکردی آنها را پیگیری میکند، اندازهگیری شدند. افرادی که دارو را مصرف میکردند، هنوز بدتر شدند اما به اندازهای که کسانی که ماده غیرفعال دریافت میکردند سریعتر نشدند. تفاوت تقریباً نیم امتیاز در این مقیاس در پایان مطالعه وجود داشت.
متخصصان درباره این تفاوت نظرهای مختلفی دارند. دکتر متیو شراگ، یک پژوهشگر نورولوژی در دانشگاه واندربیلت در تنسی، میگوید: “اغلب بیماران تفاوت را توجه نمیکنند.” شراگ و برخی پژوهشگران دیگر معتقدند که بهبود معنادار نیاز به حداقل یک امتیاز کامل در مقیاس ۱۸ امتیازی دارد. دیگران میگویند کاهش سرعت پیشرفت بیماری در مرحله اولیه – زمانی که افراد هنوز عملکرد خوبی دارند – اهمیت دارد.
دکتر رونالد پیتز، رئیس انجمن بینالمللی آلزایمر، میگوید: “اگر به تاخیر بیندازیم، ما میتوانیم زندگی بیشتری را به افراد بدهیم.” در کل، لکمبی اولین دارویی است که به تاخیر افت حافظه در بیماران آلزایمر کمک میکند. با این حال، تأیید FDA به لکمبی برای استفاده در کلینیکها و بیمارستانها ممکن است هنوز زمان ببرد و تا آن زمان، نیاز به تحقیقات بیشتر و ارزیابیهای دقیقتر برای اثبات اثربخشی و ایمنی دارو وجود دارد.
United States health officials last week approved a new Alzheimer’s drug. The drug, called Leqembi, is the first to slow the decline in memory by several months.
The Alzheimer’s Association describes Alzheimer’s as a brain disease that causes a decline in memory, thinking and reasoning skills.
One of the most common signs of Alzheimer’s disease is forgetting recently learned information or dates and events. People with the disease have difficulty doing things that they did before. Some may struggle with joining or following a discussion.
The newly approved Leqembi is a long-needed new treatment for the disease.
But experts warn that the drug is not a cure.
Dr. Joy Snider is a brain doctor at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. She said, “This drug is not a cure. It doesn’t stop people from getting worse, but it does measurably slow the progression of the disease.” She added, “That might mean someone could have an extra six months to a year of being able to drive.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the drug through a speedier-than-usual process. The process permits drugs to be launched based on early results.
The drug is only for early-stage patients and requires an injection by healthcare workers every two weeks. It is not yet clear how much the drug can help people with the disease. There are also concerns about its safety.
Still, “it’s a landmark,” said Dr. Richard Hodes, director of the National Institute on Aging. “It’s not enough, but it’s encouraging that there’s something we can do,” he added.
How does the new drug work?
Leqembi is made by Japan’s Eisai and its U.S. partner Biogen. The drug is designed to target and clear away beta-amyloid, a substance that builds up in the brain and leads to Alzheimer’s.
Dr. Sam Gandy is an Alzheimer’s expert at New York’s Mount Sinai Hospital. He told the Associated Press that Leqembi targets a slightly different form of amyloid than other drugs that have sought to treat the disease. That might explain why Leqembi proved to be successful while many other experimental drugs have failed.
In 2021, U.S. health officials approved a similar drug named Aduhelm, even though studies never proved it really helped patients. The move led to criticism after a congressional investigation.
How effective is Leqembi?
In Eisai’s 18-month study of nearly 1,800 people, Leqembi appeared to delay early-stage patients from getting worse by about five months.
The study measured people on an 18-point scale that follows their mental and functional abilities. People who got the drug still worsened but not as quickly as those given an inactive substance. The difference was nearly half a point on that scale by the study’s end.
Experts are divided over how meaningful the difference is.
Dr. Matthew Schrag is a neurology researcher at Vanderbilt University in Tennessee. He said, “Most patients won’t notice the difference.”
Schrag and some other researchers believe a meaningful improvement would require at least a difference of one full point on the 18-point scale.
Others say slowing the disease early on – when people still function well – is important.
Hodes, the director of the National Institute of Aging, said, “Several months with better cognition, what’s that worth to you?”
He added, “I think there you can get a strong argument: If I can interact with my family, be independent for months … that’s a very meaningful outcome.”
What are the risks?
Like other amyloid-targeting medications, Leqembi can cause brain swelling or small brain bleeds. In Eisai’s study, 13 percent of drug recipients had swelling, and 17 percent has small brain bleeds.
The likely reason for this is that amyloid plaques usually form around nerve cells in the brain but sometimes they get inside blood vessels, too.
Several Leqembi users died while taking the drug, including two people who were on blood-thinning medications. Eisai has said its Alzheimer’s drug did not cause their deaths.
But Gandy, the Alzheimer’s expert, said the greatest risk of serious bleeding would be among Leqembi users who take blood thinners. Older adults commonly take blood thinners to prevent or treat strokes.
Patients also may experience reactions from the drug that could include high body temperature, an upset stomach and changes in blood pressure.
Eisai says the drug should be available by January 23. A year’s worth of treatment is expected to cost $26,500. If insurance companies cover the drug, however, most people will not have to pay anywhere near that much.
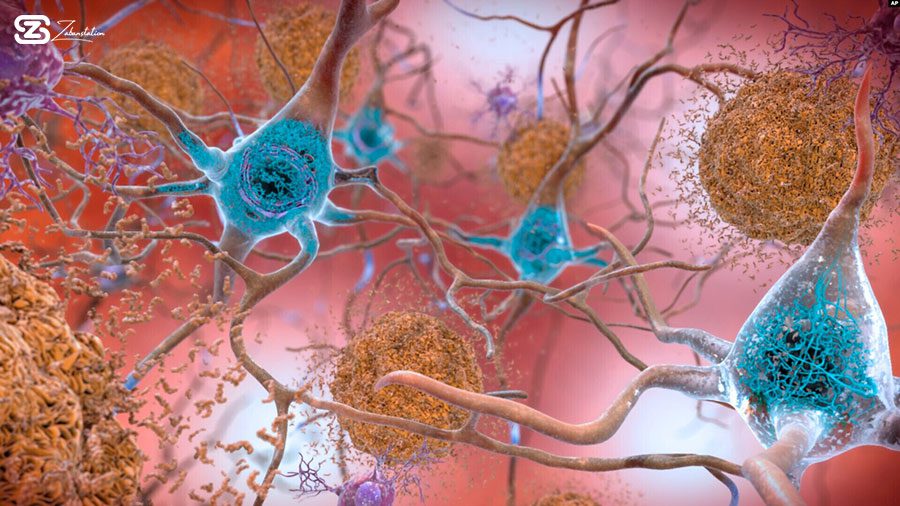
This illustration made available by the National Institute on Aging/National Institutes of Health depicts cells in an Alzheimer’s affected brain, with abnormal levels of the beta-amyloid protein clumping together to form plaques, brown, that collect between neurons and disrupt cell function. (National Institute on Aging, NIH via AP)
Words in This Podcast
لغات مهم این پادکست
decline – n. the process of become worse in condition
landmark – n. a very important achievement
encourage – v. to make something more likely to happen
scale – n. a range of numbers that is used to show size, quality or strength
cognition – n. the activity of thinking, understanding, learning and remembering
interact – v. to talk or do things with other people
outcome – n. something that happens as a result of activity or progress
swelling – n. an area on someone body’s that is larger than normal because of an illness or injury
plaque – n. a change in brain tissue that happens in Alzheimer’s disease
stroke – n. a serious illness caused when a blood vessel in your brain suddenly breaks or is blocked
Quiz – Alzheimer New Drug
آزمون پادکست انگلیسی داروی جدید آلزایمر
Like other amyloid-targeting medications, Leqembi can cause brain swelling or small brain bleeds. Patients also may experience reactions from the drug that could include high body temperature, an upset stomach and changes in blood pressure.
In Eisai’s 18-month study of nearly 1,800 people, Leqembi appeared to delay early-stage patients from getting worse by about five months.
But experts warn that the drug is not a cure. Dr. Joy Snider is a brain doctor at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. She said, “This drug is not a cure. It doesn’t stop people from getting worse, but it does measurably slow the progression of the disease.” She added, “That might mean someone could have an extra six months to a year of being able to drive.”
The drug is designed to target and clear away beta-amyloid, a substance that builds up in the brain and leads to Alzheimer’s disease.










دیدگاهها (0)